Costs and consequences of contaminated e-coat fluid in automotive manufacturing
Electrocoating (e-coat) is a cornerstone of modern automotive manufacturing, providing corrosion resistance and a uniform primer layer before painting. However, when the e-coat fluid becomes contaminated, the ripple effects can be severe—impacting product quality, operational efficiency and profitability.

What is e-coat and why does it matter?
E-coating involves immersing vehicle bodies in a water-based bath and applying an electrical charge to deposit a protective coating. This process ensures even coverage, including hard-to-reach areas and is critical for corrosion prevention and aesthetic quality. Any disruption in this system can compromise the integrity of the entire vehicle finish.
Consequences for quality
When microbiological growth is allowed to occur within e-coat fluid, it can have significant negative impacts:
- Pin-holing and cratering: Tiny holes allow moisture ingress, accelerating corrosion
- Color variations and poor adhesion: Resulting in peeling or flaking
- Structural vulnerability: Reduced durability of critical components
These defects often remain hidden until vehicles are in service, leading to warranty claims and reputational damage.
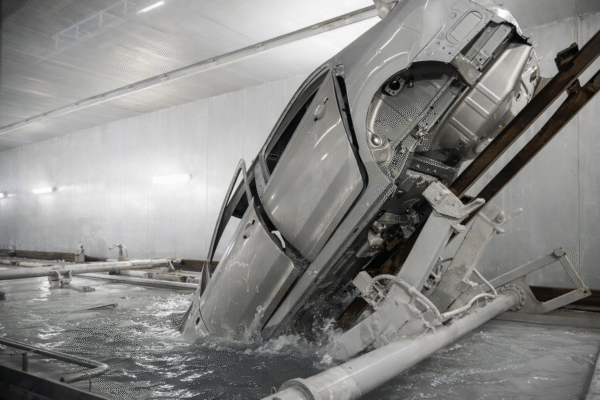
Financial impact
The costs of contamination extend far beyond rework:
- Production downtime: Emergency shutdowns for tank cleaning can halt assembly lines for weeks
- Rework and scrap: Defective bodies require stripping and recoating, consuming labor and materials
- Warranty and recalls: Corrosion-related failures can trigger expensive after-sales repairs
- Regulatory compliance: Contaminated e-coat sludge is now classified as a regulated byproduct under U.S. EPA standards, adding disposal costs and compliance risks
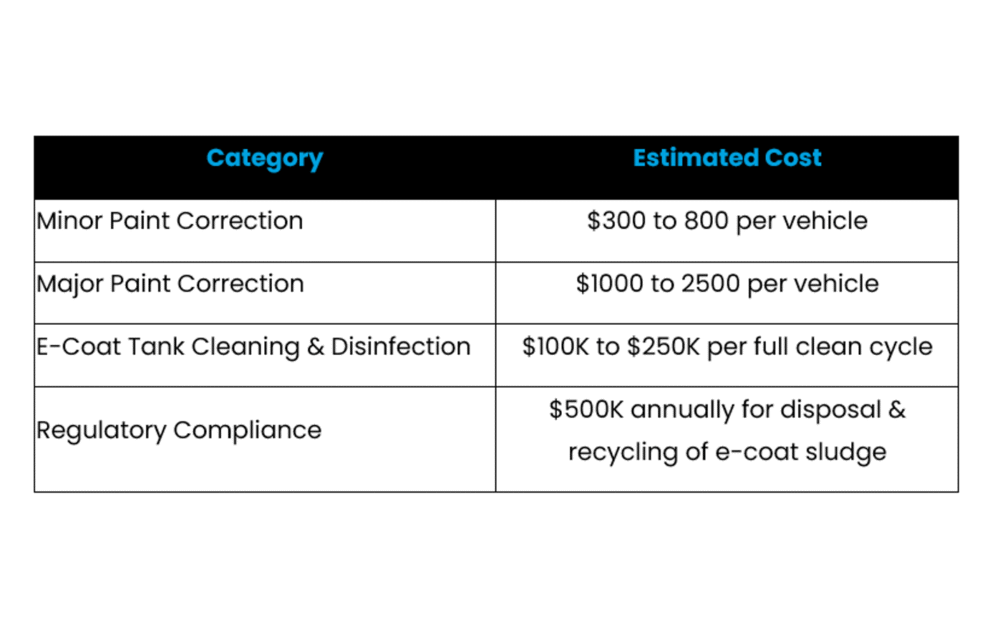
Cost breakdown at a glance
Here’s a quick snapshot of the financial impact of e-coat contamination in automotive manufacturing:
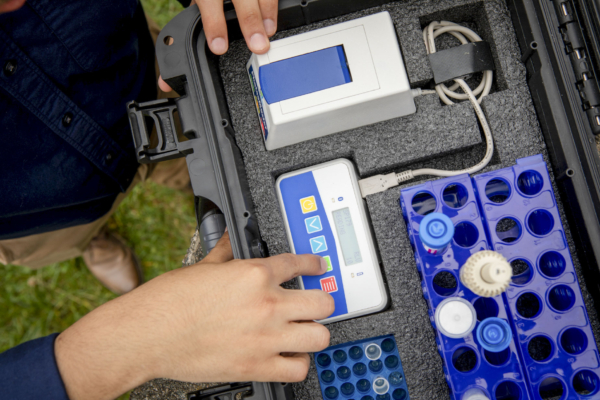
Options for Microbial Monitoring Programs
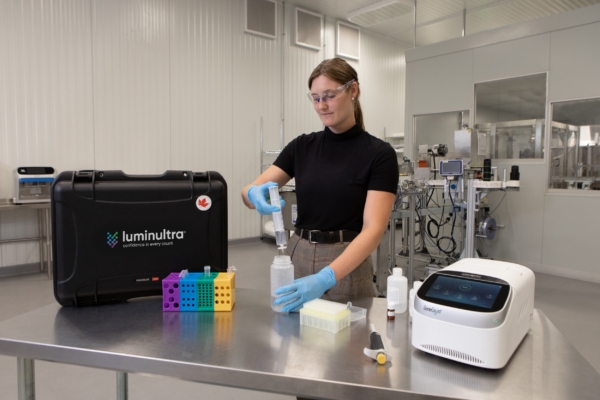
Traditional microbiological test methods take 2-10 days to acquire results, and by that time, serious problems could have already become established. Automobile manufacturers should consider rapid microbiological test methods for e-coat contamination management because they offer significant operational and financial advantages compared to traditional culture-based methods:
- Faster detection and response: Rapid methods such as ATP bioluminescence provides results in minutes rather than days, enabling immediate corrective action and preventing large-scale production issues
- Reduced downtime and cost: Early detection minimizes the need for full tank cleanouts and extended line shutdowns
- Improved quality and warranty risk mitigation: Microbial contamination in e-coat baths can lead to poor adhesion, corrosion failures, and cosmetic imperfections requiring rework. Rapid testing ensures continuous monitoring and quick intervention, reducing the risk of defects that could result in multi-million-dollar warranty claims
The bottom line
E-coat contamination is not just a technical issue—it’s a business risk. With automotive plants operating on tight margins and just-in-time schedules, any disruption can cascade into significant financial and reputational damage.
Rapid microbiological testing transforms contamination control from a reactive to a proactive process. This facilitates significant savings in time and costs while safeguarding product quality. Investing in robust contamination control measures is essential for quality assurance and long-term profitability.
Explore Luminultra resources
Make confident decisions with trusted expertise.
Discover webinars, whitepapers and expert articles focused on microbial control.